Onychomycosis(nail fungus) is a damage to the fungal infection of the nail plate and its surrounding structures: nail rollers, matrix (sprout of the nail) and nail bed.It is manifested by deformation and thickening of the nails, a change in their colors - the nails become white or yellow.
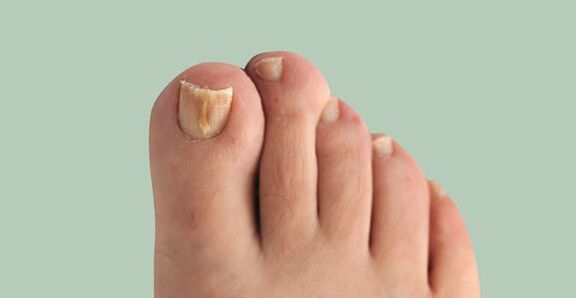
This disease is often found.The prevalence of onychomycosis in Europeans, according to some reports, reaches 10-12 %, exceeding the known indicators of the previous decade.In men, it occurs 1.5 times more often, but they contact the doctor 2 times less often than women.Older people get sick more often, children are very rare.
The main problem in the treatment of the disease is that patients come to see a dermatologist a long time after the appearance of the first symptoms.Because of this, the pathological fungus captures a large area and the treatment is delayed.
Pathogenic mushrooms can only be transmitted by a sick person.Very often, infection with a fungus occurs inside the family, since the source is not detected on time and adequate preventive measures are not carried out.
Causes of the disease:Most often, direct contact with the patient or the objects that he uses (shoes, clothes, rugs in the bathroom, washcloths, manicure supplies).Often infection occurs when visiting gyms, baths, saunas and pools.
The development of the disease is facilitated by microsences - cracks in interdigital folds that occur due to dullness, increased sweating, dry skin, poor drying after water procedures and flat feet.
Nail mycoses can also occur in the presence of concomitant diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes, obesity, hypothyroidism), vascular diseases of the limbs (venous deficiency, lymphostasis), immune disorders, as well as when using antibiotics, corticosteroid and cytostatic drugs.As a result of the above diseases, the microcirculation of blood in the nail area is disturbed and natural immunity is reduced, which contributes to the development of secondary infection.
Onychomycosis cause the following types of fungus:
- dermatophyte;
- yeast -like mushrooms of the genus Candida;
- molds.
Depending on the type of pathogen, the penetration of a fungal infection and the clinical picture are different, so the approaches to therapy are also different.
The nails on the legs are affected by a fungus 10 times more often than on hand.In most cases, dermatophytes cause the fungus (for example, Trichophyton Rubrum).The remaining cases are most often caused by inconsistent molds (aspergillus, Scopulariopsis, Fusarium).
If similar symptoms are detected, consult a doctor.Do not self -medicate - it is dangerous for your health!
Symptoms of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
The longer the disease proceeds, the more pronounced its symptoms become.The main signs of onychomycosis include:
- Dyschromia - a change in the color of the nail to yellow, black, green, gray or brown (the type of color depends on the type of mushroom);
- onycholysis - separation of the nail plate from the box;
- change in the thickness of the nail plate;
- gapalonichia - a power of the thickness of the plate and its softening;
- Koylonichia - the nail looks concave, in the form of a teaspoon;
- Pahionichia - thickening of the nail plate, hypertrophy of the nail;
- Onichogrifosis - thickening, a change in the color of the nail plate, curled in the form of a beak;
- change in the thickness of the nail bed (hyperkeratosis - thickening of the nail bed);
- Changing the surface of the nail plate: pits, furrows, crests;
- Changing the nail rollers and surrounding skin (paronychy - inflammation of the proximal nail roller).
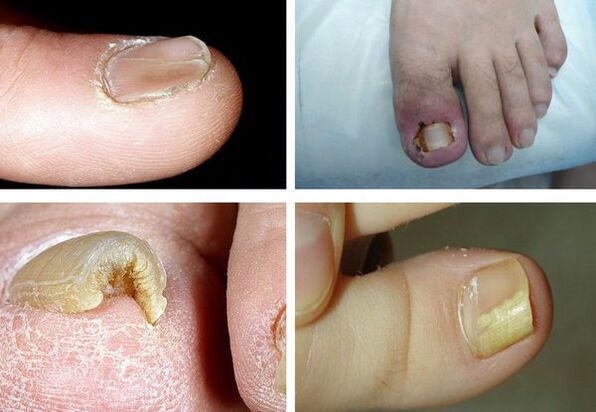
It is important to note that not one of the symptoms is pathogenic, that is, unambiguously suitable for a particular pathogen, so it is impossible to determine it by symptoms - additional examinations are needed.
Pathogenesis of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
The pathogenesis of the disease depends on how the fungus hit the skin and nails.
Distal submarine type:If the fungus is introduced through the skin in the area of the nail rollers or the distal region, then the spread of infection occurs through the free edge of the nail in the bed and further to the matrix.At first, the nail plate may not change, but later, due to hyperkeratosis, it gradually departs from the nail bed and becomes yellowish.Gradually, a thickening of the nail plate is possible.
Superficial white type:If whitish foci form on the surface of the nail, then over time, the fungus of the entire nail plate occurs.The nail thickens, crumbles, acquires a gray-brown tint.In this case, matrix and epithelium of the nail bed are not affected.There is no inflammation of the surrounding skin.
Proximal sub -gear type:The fungus can spread from the skin and periologeal rollers to the nail plate and then to the matrix, reaching the distal parts of the nail plate.Spots appear on the nail in the area of the hole and the nail bed, the nail plate is detached.There is no pronounced inflammation of the nail bed or matrix.
Total dystrophic type:The whole nail is affected.The proximal areas of the nail roller disappear or thicken, so the nail plate can no longer form and grow.
ExistsThe biophysical concept of the pathogenesis of onychomycosis, which states that with the disease, the confrontation between the two forces occurs: a fungal colony growing in the direction of the matrix, and the natural growth of the nail from the matrix to the distal edge.Therefore, the growth rate of nails is crucial during onychomycosis - the faster the nail grows, the earlier the cure comes.Perhaps this is precisely what explains the small prevalence of the disease in children, since their nails grow faster than in adults and older people.
Classification and stages of the development of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
There is the following classification of onychomycosis:
- Distal submarine;
- superficial white;
- proximal sub -gear;
- Total dystrophic.

According to the 1970 classification:
- Normotorophical: in the thickness of the nail, a strip of yellowish and whitish color, but the shape of the nail plate does not change, there is no submarine hyperkeratosis;
- hypertrophic:The nail plate turns yellow, thickens due to submarine hyperkeratosis, becomes breaking, with jagged edges;
- dystrophic:There is an thinning and removal of the nail plate from the nail bed with the formation of voids.
Complications of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
With long -existing onychomycosis, the risk of development increasesdiabetic foot(formation of trophic ulcers on the legs) andgangrene, if the patient has diabetes or vascular diseases of the lower extremities.
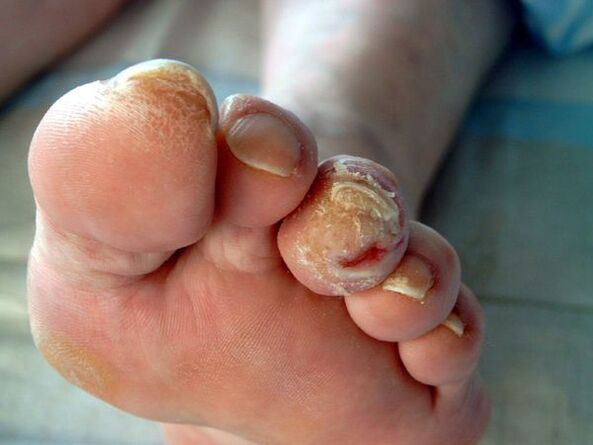
In immunosupressive conditions (primary and secondary immunodefinals), mushrooms can spread to the skin, internal organs and cause allergicization of the body.This can be manifested by rashes on the skin up to the development of bronchial asthma.
Diagnosis of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
Before disassembling the methods of diagnosis of onychomycosis, it is necessary to explain how to properly assemble the material for the study (the patient does it independently, or prepares nails before diagnostics).Before the fence of the material for the study, it is necessary to treat the nail plate with 70 % alcohol so that there is no obstruction of other bacteria.
The method of collecting material varies depending on the form of onychomycosis:
- Superficial form- make a scraping from the nail plate;
- Distant form- a scraping from the nail bed and a piece of the nail plate is necessary;
- Proximal submarine form- The material is harvested by a drill, or a biopsy of the nail is made, or a scraping from the nail bed.
The fastest method for determining pathological fungi in the nail ismicroscopy.Technique: the studied material is treated with a solution of alkali for dissolving keratin.To make the mushroom threads better, ink is added to the alkali.Next, study the resulting drug under a microscope.
This research method is the fastest and most objective.Sensitivity is up to 80 %.The disadvantages of the method include the fact that when using it, it is impossible to determine the type of pathogen.
Bacteriological sowing: is an additional method of diagnosis of onychomycosis.The material is sown on a special environment and interpreted the result under a microscope after 2-3 weeks.This method allows you to establish the type of pathogen - this helps in determining the tactics of treatment and when selecting drugs by sensitivity.But the disadvantage of the study is that it takes a lot of time, and its sensitivity is only 30-50 %.
Biopsy: With the help of a scalpel and with the use of anesthesia, a nail and a nail bed are cut off.The material is immersed in a formaldehyde solution and sent for histological examination to the laboratory.The advantages of this method are highly sensitive and allows you to determine the presence of a pathological fungus in the material.
Cons: it is impossible to identify the pathogen, as well as establish the viability of microorganisms, the high cost and complexity of the method.
Genodiagnostics: molecular biological research method (PCR).This is one of the new and highly sensitive methods for the diagnosis of onychomycosis-with the help of it, the DNA of the pathogen is revealed.It is recommended to introduce this type of diagnosis in those medical institutions that have PCR laboratories, but at the moment, test systems to identify dermatophytes and mold mushrooms only plan to introduce in the laboratory.The method allows you to determine the type of pathogen, and its sensitivity is from 80-90 %.Cons - high cost, inaccessibility, lack of technology standards and the complexity of execution.
More and more doctors are introduced into practicedermatoscopy.Using this method, you can evaluate a change in the color and structure of the nail, the condition of the surrounding structures.Dermatoscopic examination allows you to more accurately evaluate the depth of damage to the nail plate and more correctly calculate the index of the severity of onychomycosis.
Treatment of onychomycosis (nail fungus)
There are several types of treatment for onychomycosis:
- Local therapy.
- System therapy.
- Combined therapy.
- Corrective therapy.
Local therapyIt involves applying medicines to the nail plate and nail rollers.Indications for local therapy:
- Limited form of damage to the nail plate.
- There are contraindications for the appointment of systemic drugs: hypersensitivity, liver disease, kidney function, pregnancy, lactation.
The advantages of this therapy are that high concentrations of a therapeutic agent are formed on the surface of the nail, which does not penetrate the bloodstream.There are no side effects of the use of antifungal drugs - nausea, a decrease in appetite, abdominal pain.The disadvantage of the method is that the medicinal substance does not always fall into the habitat of the pathogen, especially if the mushrooms are located in the nail bed or matrix.This, in turn, can lead to inefficiency of treatment.This type of treatment is very time -consuming, since before applying the drug, it is necessary to remove the affected part of the nail.
Ways to remove affected nails:
- Mechanical removal with files, nippers or drill.
- With the help of keratolytic plasters.Before applying a keratolytic patch, the skin around the nail is sealed with a patch, a patch mass (urea with salicylic acid) is applied on top and sealed with a adhesive plaster.The patch mass is changed every 2-3 days.After each removal, the affected part of the nail is removed mechanically.
- Surgical.This operation is very painful and traumatic, since when removing the nail plate, the sprout zone can be damaged, which leads to the growth of deformed nails.
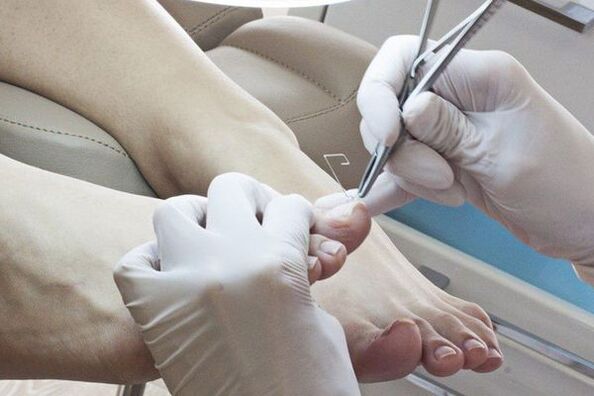
Local antifungal agents are used after removing the affected nail plate.AntimicoticsDistinguish between the place of application:
- applied to the nail: varnishes;
- Apply to rollers: creams, ointments, solutions.
The most studied tool for local use is a 1 % solution of the drug of Alllamin group, which has an evidence base in treatment in treatment based on Cocranny meta-analysis.This tool has a water base, which contributes to the better penetration of antifungal substance into the destruction site.Varnishes have a dehydrated base that reduces the penetration of the drug into deep layers.Therefore, dermatologists consider the use of varnishes unsatisfactory and more and more often prefer a water -based tool.
To get the result from local therapy, it is necessary to observe the treatment regimen, it is important for the patient to be responsible, consistent and patient.The duration of therapy can reach 12 months.
System therapyAllows the antifungal drug to penetrate through the blood at the lesion, even if the nail bed and matrix are affected.The high concentration of the drug remains for a long time in the lesion after the end of use.The disadvantages of this type of treatment are associated with the risk of side and toxic effects.
Indications for systemic therapy:
- Common forms of damage to the nail plate.
- The absence of the effect of local therapy (that is, after six months of treatment of onychomycosis on the hands and 9-12 months of treatment of onychomycosis of the feet, there was no growing healthy nails).
To determine the treatment tactics, a clinical index of the severity of onychomycosis is used.It is used as a therapeutic standard in various countries of the world.
MedicinesFor the treatment of onychomycosis, you can classify as follows:
- antimicotics - have an antifungal effect;
- Antiseptics - have both antifungal and antibacterial effects.They are rarely used, only if there are no other antifungal agents;
- Multicomponent - in addition to an antifungal agent, contain other drugs, such as anti -inflammatory.
Drug to prescribe drugs:
- standard - daily administration of drugs during the prescribed period of treatment;
- shortened - the treatment period is shortened, can be carried out by conventional doses or enlarged;
- intermittent - treatment is prescribed in several short courses, the intervals between courses are equal to the duration of the courses;
- Pulse therapy-treatment is prescribed in several short courses, intervals between courses are greater than the duration of the courses.
Antifungal drugs are divided into active substance:
- Triazols;
- Alllamins;
- Morpholins.
Currently, system therapy is usedOnly third -generation drugs.
With combined therapyLocal and systemic treatment are carried out simultaneously.Combined therapy is used if it is necessary to increase the effectiveness of systemic therapy and reduce treatment periods.
Corrective therapy(treatment of concomitant diseases): In order to select a treatment regimen, it is necessary to evaluate the general somatic state of the body.Diseases such as circulatory disorders in the limbs can reduce the access of the antifungal agent to the lesion.Therefore, drugs that improve tissue trophic are prescribed.
Due to the toxic effects of systemic antifungal drugs, it is necessary to exclude liver diseases and, if necessary, prescribe hepatoprotectors.
Forecast.Prevention
The sooner the patient contacts the doctor with signs of fungal nail lesions, the faster the disease will be cured and restore the nail plate.With long -existing processes with the capture of the entire nail, the treatment of onychomycosis can be long, but under all recommendations, recovery often occurs.If there are contraindications for systemic therapy, long -term supportive treatment with local drugs is necessary.
For preventionIt is necessary to comply with the rules of personal hygiene and reduce the possibility of re -infection:
- try to wear comfortable and high -quality shoes (in order to prevent increased sweating of the legs);
- It is recommended to change socks and tights daily;
- use only individual shoes.Those who undergo treatment for onychomycosis must be treated at the beginning of treatment, at least once a month throughout the entire treatment period and after its end;
- if necessary, use antiperspirants for the legs;
- use an individual nail care set (scissors, saws);
- Before and after visiting public places (pool, bath, sports hall), use antifungal external products (sprays, cream and pencils);
- To identify the source of fungal infection in the family and be treated at the same time.
It is recommended to periodically carry out antifungal processing of personal belongings, shoes, baths, floors and rugs.For these purposes, you can use a 40 % solution of acetic acid, 1 % alcohol solution of antiseptic (prescription is prescribed by a doctor), solutions for disinfection.Lingerie can be boiled in 1-2 % of the soap-liner solution for 20-30 minutes, ironed at maximum temperature.


















